
1,2Research Scholar, Department of AIHC & Archeology, APS University, Rewa, MP, India
DOI: 10.55559/sjahss.v1i12.74 | Received: 20.01.2023 | Accepted: 28.01.2023 | Published: 31.01.2023
ABSTRACT
The government of India is issuing a series of new coins every year, which make up a valuable aspect of the Indian currency system. Reserve Bank of India is the sole authority to designing and minting of various denominations. These coins are minted at the four Indian Government Mints at Noida (UP), Alipore (Kolkata), Cherlapally (Hyderabad), and Mumbai. Government of India issues commemorative coins to check event of incredible characters with a durable, remarkable, and exceptional contribution towards society, and so forth and to recall occasions which had extraordinary historical importance. The present study focused on the historical perspective of ₹5 commemorative coins, which was first time issued in the commemoration of Indra Gandhi. Furthermore I have examined on composition of metals, and critical analysis of these commemorative coins based on metal, weight, diameter and thickness.
Keywords: Coinage, Commemorative, Economy, Fluctuation, Mints
|
Electronic reference (Cite this article): Singh, A., & Raina, A. R. (2023). CRITICAL ANALYSIS OF INDIAN ECONOMY ON THE BASIS OF ₹5 COMMEMORATIVE COINS . Sprin Journal of Arts, Humanities and Social Sciences, 1(12), 49–64. https://doi.org/10.55559/sjahss.v1i12.74 Copyright Notice: © 2022 Author(s). This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC-BY 4.0: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), allowing third parties to copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format and to remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially, provided the original work is properly cited and states its license. |
INTRODUCTION
The establishment of credible public security depends on the financial success and prosperity of the inhabitants of any nation. In India, economic prosperity is an essential condition for improving public security and the personal satisfaction of individuals all through the nation. Many agricultural nations in the Asia-Pacific locale, including China and India where almost 33% of the total populace live, are as of now experiencing financial advances. The focal goal of progress through monetary advancement is to improve the serious effects of the economy in the worldwide commercial center to support quickened paces of financial development and subsequently constantly improve the security and prosperity of the individuals (Wadhvai, n.d., p. 259). From ancient times India is a prosperous county but its economy fluctuated from time to time.
At the outset of human development, individuals needed to deliver or obtain their necessities by dint of their work. In course of time, the act of trade came into vogue. In the crude barter system, there was the issue of discovering "two people whose confiscate capable belongings commonly fit every others' needs. There might be numerous people needing and having those things needed, yet to permit a demonstration of trade, there should be a two folds co-rate, which will seldom occur". In advantageous norms, various metals were utilized in the field. In India gold, silver and copper were used for exchange since ancient times. The development of cash has gone through the accompanying stages relying on the advancement of human progress at various occasions and places. They are product cash (system of barter), metallic money (evolution of coinage), paper currency (evolution of banknotes), and credit cash (money), plastic money (payment system through cards), and polymer banknotes (plastic money) (Chinnammai, 2023, p. 43).
COMMEMORATIVE COINS
Indian coinage has assumed a unique place in history, in spheres of political and economic changes from the earliest times. Not only coins provide traces about trades and commerce as well as about the economic development of the times. The earliest coins of India were Punch marked dared back to 6th- 7th Century B.C. after then coins issued by the imperial dynasties and small kingdoms began all over the Indian Sub-continent. Indo Greeks were the first who issued commemorative coins in India. Silver coins of Azes I and Azilises, particularly of the previous, are abundant As on Maues' coinage, Greek divine beings and goddesses, Zeus, Herakles, Pallas, and Poseidon, show up on both silver and copper of these two rulers, but unexpectedly an Indian goddess, Lakshmi, is introduced first time (Brown, 1922, p. 28). Chandragupta I, Introduce Archer coins in which goddess Lakshmi sits upon a lotus rather than a throne, and in the subsequent kind, other than the replacement of a lion for a tiger, and change on the reverse side in which, Lakshmi being situated on a lion in different perspectives (Brown, 1922, p. 43). During the early medieval period, Muhammad Ghori had ventured the figure of Lakshmi on his gold coins and put its name in Nagari characters (Gupta, 1969, p. IX). At the beginning of the 50th regnal year of Akbar, he issued gold and silver coins where the portrayal of Rama and Sita with the words Rama-Siya in Nagari is seen on one side of the coin (Gupta, 1969, p. 119). In Modern times Britishers gave the coins in sequential request, the issues after 1840, having the portraits of Queen Victoria. It was in 1862 when coins were given under the crown and in 1877 sovereign Victoria assumed the title of 'sovereign of India'. Interestingly the legacy of the commemoration of coins continued after the independence of India, where we see several coins issued in commemoration of different influential personalities.
According to the Coinage Act, 2011 "commemorative coins" signifies any coin stamped by the Government or some other authority enabled by the Government for this sake to recognize a particular event or occasion and communicated in Indian currency. As needs are, the Government issues memorial coins to check event of incredible characters with a durable, unique, and outstanding contribution towards society, and so forth and to recall occasions which had extraordinary historical importance, according to Guidelines affirmed by the Government (Report, 2018-19, p. 62). From 1992 onwards 5 rupees copper-nickel coins were issued for the first time in India. In 1985 First commemorative coin was issued by the Government of India in the commemoration of Indra Gandhi. After that, the processes of issuing commemorative coins continue till now. From time to time Govt. of India issued commemorative coins of legendary personalities and important historical events, these coins are made up of different metals and there are lots of variations in these coins also.
LIST OF COMMEMORATIVE COINS ISSUED BY GOVERNMENT OF INDIA
|
S. No |
Year |
Commemoration |
Mint |
Composition of Metals |
Diameter Mm |
Thickness Mm |
Weight gm |
|
1 |
1985 |
Indira Gandhi |
HM |
CuNi |
31.1 |
2.3 |
12.6 |
|
2 |
1989 |
Jawaharlal Nehru |
HM |
CuNi |
31.1 |
2.3 |
12.6 |
|
3 |
1991 |
Commonwealth Parliamentary Conference |
M |
CuNi |
31.00 |
12.50 |
|
|
4 |
1991 |
Tourism Year. |
M |
CuNi |
31.00 |
12.50 |
|
|
5 |
1994 |
World of Work (ILO)1919-1994 |
HMN |
CuNi |
23.3 |
2.6 |
8.9 |
|
6 |
1995 |
8th World Tamil Conference (St. Thiruvalluvar) |
MN |
CuNi |
23 |
2.94 |
9.13 |
|
7 |
1995 |
50th Anniversary of UNO |
MN |
CuNi |
2.3 |
2.9 |
9.18 |
|
8 |
1995 |
Food & Agriculture Organization (1945-1995) FAO |
HMN |
CuNi |
23 |
3 |
9 |
|
9 |
1996 |
Mother's Health is Child's Health |
KHMN |
CuNi |
23 |
2.85 |
8.97 |
|
10 |
1996 |
International Crop Science |
K |
CuNi |
23 |
9 |
|
|
11 |
1997 |
Inter-Parliamentary Conference-Men and Women Partnership in Politics |
CuNi |
23 |
9 |
||
|
12 |
2001 |
Bhagwan Mahavir: 2600th Janm Kalyanak |
MN |
CuNi |
23.19 |
2.77 |
9.07 |
|
13 |
2003 |
Dadabhai Naoraji (1825-1917) |
KHM |
CuNi |
23 |
9 |
|
|
14 |
2004 |
Kumarasami Kamraj (1903-1975) |
KHM |
CuNi |
23.6 |
2.9 |
8.9 |
|
15 |
2004 |
Lal Bahadur Sastri (1904-2004) |
K |
CuNi |
23 |
9 |
|
|
16 |
2004 |
Lal Bahadur Sastri (1904-2004) |
KHM |
SS |
23 |
6 |
|
|
17 |
2005 |
Dandi March Years Of Dandi March (1930-2005 |
M |
CuNi |
23 |
8.85 |
|
|
18 |
2005 |
Dandi March Years Of Dandi March (1930-2005 |
M |
SS |
23 |
6 |
|
|
19 |
2006 |
Mahatma Basaveshwara |
M |
CuNi |
23 |
3 |
9 |
|
20 |
2006 |
Mahatma Basaveshwara |
M |
SS |
23 |
2 |
6 |
|
21 |
2006 |
ONGC 50 Celebrating India (1956-2006) |
K |
CuNi |
23 |
9 |
|
|
22 |
2006 |
ONGC 50 Celebrating India (1956-2006) |
KH |
SS |
22.8 |
2.13 |
6.03 |
|
23 |
2006 |
Sree Narayan Gurudev |
M |
CuNi |
23.1 |
9.5 |
|
|
24 |
2006 |
Sree Narayan Gurudev |
M |
SS |
22.9 |
2.13 |
6.03 |
|
25 |
2006 |
SBI (1806-2006) |
K |
CuNi |
23 |
9 |
|
|
26 |
2006 |
SBI (1806-2006) |
KH |
SS |
23 |
2.13 |
6 |
|
27 |
2007 |
150th B. Anni. of Lokamanya Bal Gandhar Tilak Hindi |
M |
CuNi |
23 |
9.5 |
|
|
28 |
2007 |
150th B. Anni. of Lokamanya Bal Gandhar Tilak |
M |
SS |
23 |
6 |
|
|
29 |
2007 |
150th B. Anni. of Lokamanya Bal Gandhar Tilakji |
M |
CuNi |
23 |
9 |
|
|
30 |
2007 |
150 Years First War of Independence |
M |
CuNi |
23 |
9 |
|
|
31 |
2006 |
150 Years First War of Independence |
M |
SS |
23 |
6 |
|
|
32 |
2007 |
Khadi & Village Industries (CuNi) |
M |
CuNi |
23 |
9.5 |
|
|
33 |
2007 |
Khadi & Village Industries (SS) |
M |
SS |
23 |
6 |
|
|
34 |
2009 |
Saint Alphonsa Birth Centenary (1910-2009) |
KHM |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
6 |
|
|
35 |
2009 |
Perarignar Anna Cen. (1909-2009) |
KHM |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
6 |
|
|
36 |
2009 |
60 years of Commonwealth |
KHM |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
1.9 |
6 |
|
37 |
2009 |
25th Birth Anni. Of Dr. Rajendra Prasad (1884-2009) |
KHMN |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
6 |
|
|
38 |
2010 |
Reserve Bank of India Platinum Jubilee (1935-2010) |
HM |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
2 |
6 |
|
39 |
2010 |
XIX Commonwealth Games |
KHMN |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
6 |
|
|
40 |
2010 |
C. Subramaniam Birth Cent. (1910-2010) |
KHMN |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
2 |
6 |
|
41 |
2010 |
1000 Yr Of Brihadeswarar Temple Thanjavur |
KHMN |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
6 |
|
|
42 |
2010 |
Mother Teresa Cent. (1910-2010 |
KHMN |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
1.9 |
6 |
|
43 |
2010 |
Comptroller & Auditor General |
KHMN |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
1.9 |
6 |
|
44 |
2011 |
Income Tax – Chanakya 150 Years of building India (1860-2010 |
KHMN |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
2.1 |
6 |
|
45 |
2011 |
100 Yrs. of Civil Aviation India (1911-2011) |
KHMN |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
2 |
6 |
|
46 |
2011 |
Rabindra Nath Tagore |
KHMN |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
1.9 |
6 |
|
47 |
2011 |
6 Indian Council of Medical Research - Cen. Year (1911- 2011) |
KHMN |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
6 |
|
|
48 |
2011 |
150th Birth Anniv. Of (1851-2011) Madan Mohan Malviya |
KHMN |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
1.9 |
6 |
|
49 |
2012 |
60 Years of the Parliament of India |
M |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
6 |
|
|
50 |
2012 |
Shaheed Bhagat Singh Birth Cent. (1907-2007) |
KHMN |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
6 |
|
|
51 |
2012 |
Shri Mata Vaishno Devi Shrine Board |
HMN |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
6 |
|
|
52 |
2012 |
60 Years of India Govt. Kolkata Mint (1952-2012) |
KHMN |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
2 |
6 |
|
53 |
2012 |
150th Anni. Of Motilal Nehru Bom |
KHMN |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
1.9 |
6 |
|
54 |
2013 |
150th Years of Kuka Movement (1857-2007 |
KHMN |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
6 |
|
|
55 |
2013 |
150th Birth Anniv. Of Swami Vivekananda (1863-1902) |
KHMN |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
6 |
|
|
56 |
2014 |
Acharya Tulsi Birth Cent. (1914-2013) |
KHMN |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
1.9 |
6 |
|
57 |
2014 |
125th Anni. Of Maulana Abdul Kalam Azad (1888-1958) |
KHMN |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
6 |
|
|
58 |
2014 |
125th Birth Anni. Of Jawaharlal Nehru (1889-2014) |
KHMN |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
1.9 |
6 |
|
59 |
2014 |
Cent. Of Komata Maru Incident (1914-2014 |
HMN |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
1.9 |
6 |
|
60 |
2015 |
175th Birth Anni. Jamsherji Nusserwanji Tata (1839- 2014) |
KM |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
6 |
|
|
61 |
2015 |
Begum Akhtar Birth Century (1914-2014) |
KM |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
2 |
6 |
|
62 |
2015 |
Birth Anni. Of Rani Gaidinliu (1915-2015) |
K |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
2 |
6 |
|
63 |
2015 |
Golden Jubilee 1965 Operations- 1st Strike |
M |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
2 |
6 |
|
64 |
2015 |
Golden Jubilee 1965 Operations 2nd Strike |
KMHN |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
2 |
6 |
|
65 |
2015 |
BHEL - 50 Years of Engineering Excellence (1964-2014) |
KM |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
1.8 |
6 |
|
66 |
2015 |
Biju Patnaik Birth Cent. (1916-2016 |
K |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
2 |
6 |
|
67 |
2016 |
150th Anni. Of Allahabad High Court (1866-2016) |
HM |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
2 |
6 |
|
68 |
2016 |
The University of Mysore Cent. Celebrations (1916-2016 |
M |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
2 |
6 |
|
69 |
2016 |
Birth Cent. Of Pandit Deendayal Upadhyaya |
M |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
1.9 |
6 |
|
70 |
2016 |
Shri Krishna Chaitanya Mahaprabhu |
M |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
2 |
6 |
|
71 |
2017 |
M.G.Ramachandran Birth Century |
KHMN |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
2 |
6 |
|
72 |
2018 |
125th Birth Anni. Prasanta Chandra Mahalanobis |
K |
Ni-Brass |
23 |
2 |
6 |
Sources: RBI Press Releases, RBI Annual reports, (Wikipedia, n.d.) (Numista, n.d., pp. 7-11)
COMPOSITION OF METALS
Three types of metals are used in 5rs commemorative coins in India
Diameter 23mm and weight 6gm
Diameter 23mm and weight 6gm
As per the Coinage Act of 1906, Govt. India has sole authority for issuing coins and currency. The planning and printing of coins in different groups is additionally the duty of the Government of India. These coins are minted in five Government mints which are in Mumbai, Noida (UP), Cherlapally and Saifabad (Hyderabad), and Alipore (Kolkata). We can identify these mints based on their mints marks. As per the RBI Act, different types of material were used such as Copper-Nickel (CuNi), Stainless Steel (SS), and Nickel-Brass (Ni-Brass). From 1985 to 2007 copper-Nickel metal was used, but there is some variation in shape and size of these coins. In the first phase (1985-1991) RBI issued four commemorative CuNi coins containing 75% Copper and 25% Nickel with diameter 31.1 and 31.00 and weight 12.60 and some coins weight are 12.50. In the second phase of (1994-2007), RBI issued twenty commemorative coins of CuNi, whose diameter is about 23.3 and some coins have 23mm and the weight is 9.18 and some coins have 8.85. From 2004-2010 SS (Stainless steel) eleven commemorative coins were issued by RBI which contain Ferritic Stainless Steel Iron - 82% Chromium - 18%, having diameter 23mm and weighs 6gm. From 2009-2018 Ni-Brass Nickel-Brass metal was used which contains 75% copper and 25% Nickel and having a diameter of 23mm and weighs 6gm.
ANALYSIS OF 30 CIRCULATING 5 RUPEES COMMEMORATIVE COINS

|
S. No |
Years |
Commemoration |
Mint |
Weight gm |
Absorbed weight gm |
Diameter Mm |
Absorbed Diameter Mm |
Thickness mm |
Absorbed Thickness mm |
|
1 |
1985 |
Indira Gandhi |
H, M |
12.6 |
12.5 |
31.1 |
31.1 |
2.3 |
2.4 |
|
2 |
1995 |
Food & Agriculture Organisation (1945-1995) |
N |
9.0 |
9.0 |
23 |
23 |
3 |
2.9 |
|
3 |
1996 |
Mother's Health is Child's Health |
H |
8.97 |
8.95 |
23 |
23.1 |
2.85 |
2.8 |
|
4 |
2003 |
Dadabhai Naoraji (1825-1917) |
N, N |
9.00 |
9.20 8.85 |
23 23 |
23 23 |
…… |
2.6 2.5 |
|
5 |
2004 |
Kumaraswamy Kamraj (1903-1975) |
H |
9.00 |
9.10 |
23 |
23 |
2.9 |
2.8 |
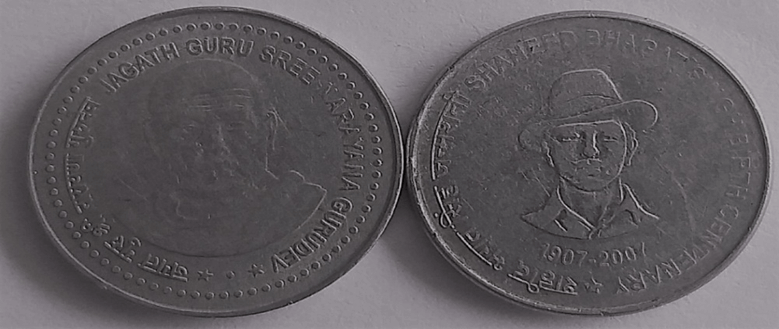
|
S. No |
Years |
Commemorative |
Mint |
Weight |
Absorbed weight |
Diameter |
Absorbed Diameter |
Thickness |
Absorbed Thickness |
|
1 |
2006 |
Jagat Guru Sree Narayan Gurudev |
N |
6.03 |
6.05 |
22.9 |
22.9 |
2.13 |
2.1 |
|
2 |
2007 |
Shaheed Bhagat Singh Birth Cent. (1907-2007) |
H |
6.00 |
6.10 |
23 |
22.8 |
…….. |
2.1 |

|
S. No |
Years |
Commemorative |
Mint |
Weight |
Absorbed weight |
Diameter |
Absorbed Diameter |
Thickness |
Absorbed Thickness |
|
1 |
2009 |
125th Birth Anni. Of Dr. Rajendra Prasad (1884-2009) |
N |
6.00 |
5.90 |
23 |
22.8 |
2 |
1.7 |
|
2 |
2010 |
1000 Yr Of Brihadeswarar Temple Thanjavur |
H H |
6.00 6.00 |
5.95 6.00 |
23 23 |
23 23 |
2 2 |
1.7 1.7 |
|
3 |
2010 |
Comptroller & Auditor General |
N |
6.00 |
5.95 |
23 |
23.1 |
1.9 |
1.7 |
|
4 |
2011 |
Mother Teresa Cent. (1910-2010 |
K |
6.00 |
5.90 |
23 |
22.9 |
1.9 |
1.8 |
|
5 |
2011 |
Income Tax 150 Years of building India (1860-2010 |
M |
6.00 |
5.95 |
23 |
23 |
2.1 |
1.7 |
|
6 |
2011 |
Rabindra Nath Tagore |
K |
6.00 |
5.85 |
23 |
22.8 |
1.9 |
1.7 |
|
7 |
2011 |
6 Indian Council of Medical Research - Cen. Year (1911- 2011) |
H |
6.00 |
6.20 |
23 |
23 |
2 |
1.8 |
|
8 |
2012 |
150th Anni. Of Motilal Nehru Born |
N |
6.00 |
5.95 |
23 |
23.1 |
1.9 |
1.8 |
|
9 |
2012 |
Shri Mata Vaishno Devi Shrine Board |
N N N N N |
6.00 |
6.00 5.95 6.00 5.90 5.90 |
23 |
23.1 23 23.1 23 23 |
2 |
1.8 1.8 1.8 1.7 1.8 |
|
10 |
2012 |
60 Years of the Parliament of India |
H |
6.00 |
6.00 |
23 |
23.1 |
2 |
1.7 |
|
11 |
2013 |
150th Birth Anniv. Of Swami Vivekananda (1863-1902) |
M M H |
6.00 |
5.95 5.95 6,05 |
23 |
23.1 23 23 |
2 |
1.8 1.9 1.8 |
|
12 |
2014 |
125th Birth Anni. Of Jawaharlal Nehru (1889-2014) |
H |
6.00 |
6.00 |
23 |
23 |
1.9 |
1.8 |
|
13 |
2014 |
125th Anni. Of Maulana Abdul Kalam Azad (1888-1958) |
M |
6.00 |
5.90 |
23 |
23 |
2 |
1.8 |
|
14 |
2015 |
175th Birth Anni. Jamsherji Nusserwanji Tata (1839- 2014) |
M |
6.00 |
6.10 |
23 |
23.1 |
2 |
1.9 |
|
15 |
2016 |
150th Anni. Of Allahabad High Court (1866-2016) |
K |
6.00 |
5.95 |
23 |
22.9 |
2 |
1.8 |
H-Hyderabad Mint, M-Mumbai Mint, N-Nodia Mint, K-Kolkata Mint
ANALYSIS OF METAL
In the history of Indian coinage different coins were issued by the Government of India, commemorative coins are one among them. These coins were commemorated in the memory of legendary personalities, who play a significant role in the development of the country and some coins were issued for particular events. From time-to-time various types of metals/material were used in these coins. Firstly copper-Nickel (CuNi) was used which contains 75% of copper and 25% Nickel. After that, Stainless Steel (SS) metal is used in the minting of coins which contain Ferritic Stainless-Steel Iron - 82% Chromium - 18%. Thirdly Nickel-Brass (Ni-Brass) coins contain Copper - 75% Nickel - 25%.
WEIGHT
In the history of Indian commemorative coins India, the first five rupees commemorative coins were issued by Govt. of India in 1985. As per RBI guidelines, every coin has an equal weight. But with time metals and weight of these coins got changed. In 1985, Copper-Nickel metals were used and weighed 12.60/50. The second phase of Copper-nickel commemorative coins was started in 1994 when the weight of coins was reduced 9gm by RBI. In 2004, Stainless stains metals were used with weighting 9gm, and in 2009 Nickel-Brass coins were issued with a weight of 6 gm. while studying these coins there is a lot of variation in the size of these coins. Few instances the numbers of coin's weights are higher than the actual weight.
DIAMETER AND THICKNESS
Likewise, the metal, weight, Diameter, and Thickness of these commemorative coins also got changed by the RBI. In 1984, Copper-Nickel commemorative coins having a diameter of 31.1 and thickness of 2.3, but in 1994, the diameter and weight of copper-nickel commemorative coins changed Diameter 23.3/23 and weight 19.18/8.85. After copper-nickel stainless steel coins were introduced in which diameter are 3mm and thickness are 2mm, and same diameter thickness is in Nickel-Brass coins. But during the analysis I got, the diameter and thickness of some coins are greater than their actual size.
FINDINGS
While observing these commemorative coins there is a lot of fluctuation of an economy based on metal, weight, thickness, and diameter. The government of India issued the first copper-nickel commemorative coin in the commemoration of Indira Gandhi weighing 12.6 gm, diameter 31.1 mm, and thickness 2.4mm. In 1995 commemorative coins got some variation in shape and size, which weighted 9gm, diameter 23 mm, and thickness 3mm. in 2006 the Stainless-steel coins weighing 6.03gm, diameter 22.9mm, and thickness 2.31mm. In 2009, Nickel-Brass coins are found to weight 6gm, diameter 23mm, and thickness of 2mm. these coins show that there is the fluctuation of Indian economy, firstly the weight of coins is 12.6 gm then 9gm and finally, it reached to 6 gm. With time, there was a change in the metal, initially, it was copper, but the latter was replaced by nickel and brass. Based on the above analysis and the changes in metal, weight, diameter, and thickness indicate the fluctuation in Indian coinage based on 5 rs commemorative coins.
Brown, C. J. 1922. The Coins of India. Calcutta: Associate Press.
Chinnammai, S. 2023. A Study on Currency and Coinage Circulation in India, International Journal of Trade, Economics and Finance, Vol. 4( No. 1), pp. 43-47.
Gupta, L. B. &. S. 2002. Elementary Numismatic studies coins of India from 1835-2002, Gurgaon: Kaproori Devi Charitable trust.
Gupta, P. L. 1969. Coins. New Delhi Inda: National Book Trust.
Numista, n.d. Coins from India. [Online]
Available at: en.numista.com
RBI, 31-12-2008. New Cupro Nickel Coin of Rs. 5 – "Jagath Guru Sree Narayana Gurudev
RBI, 01-03-2010. Press release, Platinum Jubilee of Reserve Bank of India issue of Commemorative Coin Set
RBI, 10-04-2010. Press release, New commemorative circulation coin of Rs.5/- denomination (Nickel Brass) on the occasion of "60 years of the Commonwealth"
RBI, 12-06--2012. Press release, Issue of coins to commemorate the occasion of "60 years of the Parliament of India
RBI, 12-09-2007. Press release, New Coins of Rs.5/- in Cupro-Nickel (CN) to commemorate the occasion of "150 years – The First War of Independence
RBI, 12-11-2010. Press release, Issue of new coins with the theme "PLATINUM JUBILEE OF RESERVE BANK OF INDIA"
RBI, 24-10-2008. Press release, New Coins of Rs.5/- in Cupro-Nickel (CN) to commemorate the occasion of "Golden Jubilee Celebration of Khadi and Village Industries Commission
RBI, 31-10-2007. Press release, New Cupro-Nickel Coin of Rs.5 – to Commemorate the Occasion of 150 Birth Anniversary of Lokmanya Bal Gangadhar Tilak
Report, A., 2016-17. Government of India Minister of Finance
Report, A., 2018-19. Government of India, Minister of Finance
Vincent, 2020. World of Coins, Elusive copper-nickel commemorative coins of India, 2000-2008. [Online]
Available at: www.worldofcoins.eu
[Accessed 27 October 2020].
Wadhvai, C. D. n.d. India trying to liberalism, Economic reforms since 1991. 1991.
Wikipedia, n.d. Coins of the Indian Rupee. [Online]
Available at: en.wikipedia.org