1,2,3Faculty, College of Education, Jose Rizal Memorial State University, Philippines
DOI: 10.55559/sjahss.v2i02.91 | Received: 06.03.2023 | Accepted: 11.03.2023 | Published: 17.03.2023
ABSTRACT
Results in the Licensure Examination for Teachers are contributory to the institutional overall performance, hence, analyzing the results is essential. Results of the 67 takers who took the examination from 2015 to 2017 were analyzed. Employing Mean, t-test, and Pearson Moment Correlation, the results revealed that the performance of both BSED and PEC Graduate Takers in General Education Courses is higher compared to Professional Education Courses, there is a significant difference in the results of the Licensure Examination for Teachers in both the General Education and Professional Education Courses among BSEd and PEC Graduate Takers. Also, there is a significant relationship between the general education course result and professional education course result. It also revealed that the general education course results and professional education course results are directly proportional. It means as general education course result is high, the professional education course result will follow. On the other hand, if general education course result is low; the professional education course result is also low.
Keywords: BSEd graduate takers, PEC graduate takers, LET, General Education Course, Professional Education Course
|
Electronic reference (Cite this article): Murro, R. A., Divinagracia, L. T., & Inoferio, H. V. (2023). RESULTS IN THE LICENSURE EXAMINATION FOR TEACHERS: AN ANALYSIS. Sprin Journal of Arts, Humanities and Social Sciences, 2(02), 50–60. https://doi.org/10.55559/sjahss.v2i02.91 Copyright Notice: © 2023 Author(s). This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC-BY 4.0: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), allowing third parties to copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format and to remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially, provided the original work is properly cited and states its license. |
Introduction
One of the College of Education's top aims is to maintain and improve its graduates' passing rates on the Licensure Exam for Teachers (LET). It is an example of the high level of education provided by that Higher Education Institute (HEI), specifically a Teacher Education Institution (TEI) (Alova, 2021). The performance of graduates in board examinations is used to assess the quality of a program. Teaching in the Philippines is governed by legislation and regulated by the Professional Regulatory Commission (PRC).
To be eligible for public school teaching, education graduates must pass the Licensure Examination for Teachers (LET). As a result, the LET establishes the minimal standard for teaching and is regarded as a barometer of the quality of pre-service teacher education. A higher LET passing rate indicates a greater quality of pre-service teacher education and a low LET passing rate indicates inadequate pre-service teacher education. If the first try pass rate is high, it is a good indicator of program excellence (Professional Regulation Commission CHED, 2004). Increasing the percentage of passing in the Licensure Examination for Teachers is always the priority of the Teacher Education Institutions.
Philippines recognizes the vital role of teachers in nation-building and development through a responsible and literate citizenry. Towards this end, the state shall ensure and promote quality education through proper supervision and regulation of the licensure examination and professionalization of the practice of the teaching profession (Philippine Teachers Professionalization Act of 1994, 2017).
In compliance with the Republic Act 7836 (The LET Law) and with Article II of Commission on Higher Education Memorandum Order (CMO) No. 30, S. 2004, graduates of non-education degrees shall take 18 units of professional education courses, and 12 units of experiential learning courses (Field Study and Practice Teaching) to qualify for the Licensure Examination for Teachers. Thus, universities and colleges offered the Professional Education Certificate Program. The program is designed for degree holders who wish to pursue in teaching career. The program comprises the professional education component of the teacher education program required by both Commission on Higher Education and the Professional Regulations Commission. Any holder of a bachelor's degree may apply for admission to the program. Graduates of the program are anticipated to gain knowledge and skills in curriculum creation, instruction delivery, classroom management, and evaluation, preparing them for a career in teaching.
To ensure that only qualified instructors can be hired, licensing is necessary. The Licensure Examination for Teachers (LET) is a test of the general knowledge and proficiency of prospective teachers. It offers a trustworthy framework within which their practice can be evaluated and confirmed (Guinayen, 2014). LET is currently the most-numbered examinee being administered by the Professional Regulation Commission. The exams are scheduled twice a year to cater to the growing number of aspiring registered professional teachers for both elementary and secondary levels.
Passing the Licensure Examination for Teachers is one of the key benchmarks for teacher education graduates to qualify as professional teachers as mandated in RA 7836, commonly known as the "Philippine Teachers Professionalization Act of 1994." Aspiring teachers who have completed their Bachelor of Secondary Education (BSEd) are tested in the LET along three components, namely General Education, Professional Education, and Field of Specialization, with weights of 20%, 40%, and 40%, respectively.Graduates of the Bachelor of Elementary Education (BEEd) program, on the other hand, are evaluated along two components: General Education and Professional Education, with weights of 40% and 60%, respectively. The LET has a 75% passing rate. Passing this standardized test is not only a necessity for teaching, but it also ensures that teachers in the primary school sector have the essential competence and professional accountability (Amanonce & Maramag, 2020).
(Chua et al., (2019), found out that the review program is somehow successful at the end of the study. Participants are ready to take the LET. The study recommends pursuing the mentoring and coaching program for the next batches of 4th-year students; however, there is a need to modify some procedures and strategies in the program for further improvement and to meet the specific needs of the reviewees. Moreover, Tan et al. (2015) argued that graduates’ performance in the licensure examination reflects the quality of education and training provided by their schools.
Jose Rizal Memorial State University-Katipunan Campus (JRMSU) College of Education ensures that the passing percentage in the Licensure Examination for Teachers should be more than the national passing percentage. With this target, procedures, strategies and other coaching program should be enhanced or developed, thus this study has to be conducted and the findings of the study will provide data as bases in developing review program and other instructional strategies of the college of education.
Objectives
This study aimed to determine the performance of the Bachelor of Secondary Education (BSEd) Graduate Takers and the Professional Education Certificate (PEC) Program Graduate Takers in the Licensure Examination for Teachers (LET) of Jose Rizal Memorial State University-Katipunan Campus in terms of General Education and Professional Education from 2015 to 2017. The results of this study will serve as bases in developing a review program and enhancing procedures and strategies for quality instructional delivery of the college of education.
Specifically, it aimed to (1) determine the significant difference on the results incurred by the Bachelor of Secondary Education Graduate Takers and Professional Education Certificate (PEC) Program Graduate Takers in General Education Courses; (2) describe the significant difference on the results incurred by the Bachelor of Secondary Education Graduate Takers and Professional Education Certificate (PEC) Program Graduate Takers on Professional Education Courses; (3) determine the significant relationship between the general education and professional education LET results of 2015, 2016 and 2017 among Education Graduates and PEC Graduates; and (4) recommend outputs based on the findings.
Theoretical/Conceptual Framework
This study is based on Martin Ford's Motivational Systems Theory (MST) which focuses on the individual as the unit of analysis but embeds the individual in the biological, social, and environmental contexts that are crucial to development. Ford proposed a simple mathematical formula that attempts to represent all these factors in one model:
Performance = Ability x Motivation
The above formula indicates that a student with very high ability, but low motivation is unlikely to perform well, whereas a student with low ability but high motivation is likely to perform well. That is, the variability in motivation across students may dampen associations between ability and performance. In the same vein, one can argue that it is simply the study habits and attitudes that ultimately bring about the desired performance and not students' inner desires or motivations. Therefore, similar to how motivation interacts with the ability to influence academic performance, one can infer that study habits and attitudes interact with the ability to influence student performance in board examinations. Board Exam Performance = Ability x (Study Habits and Attitudes).
Another theoretical framework of this study is based on Wiener’s Attribution Theory (Weiner, 1974) and Cronbach and Snow’s Aptitude Treatment Interaction Theory (Cronbach & Snow, 1989). The Attribution Theory of Weiner outlines a method for scrutinizing and understanding motivation and achievement in the academe, which is appropriate for the study at hand.
On the other hand, according to the Aptitude-Treatment Interaction (ATI) theory, there are some instructional strategies (treatments) which are more or less effective for particular individuals or groups only depending upon their specific abilities. ATI suggests that optimal learning can be achieved when the instruction is exactly matched to the abilities of the learner.
The framework of the study is anchored on the premise that success or failure of a student taking an examination, particularly a board or licensure examination depends greatly on several factors such as being a graduate of BSEd or a graduate of Professional Education Courses Program and the knowledge in General Education and Professional Education Courses as perceived by the reviewers and the reviewees and those who have successfully passed the examination already.
Rabanal (2016) analyzed the performance of BEEd graduates in the University of Northern Philippines. Her study likewise revealed that academic achievements in general education, professional education and major courses were significantly related to the different test components in the board examination. The findings of Garcia (2013), deviated slightly from those mentioned above in professional education courses where a weak positive correlation with LET performance was noted.
Thus, this study determines the performance in the Licensure Examination for Teachers of both graduates of BSED and the graduates of the program Professional Education Certificate in general and professional education courses only.
Methodology
The study included all of the LET takers from 2015 to 2017. This study employed the analytical method of research, documentary analysis of data taken from the official results of the Licensure Examination for Teachers released by the Professional Regulatory Commission (PRC) of the Professional Education Certificate (PEC) Program completer takers.
A total sampled population of 67 takers from 2015 to 2017 were considered respondents of the study. Only results in General Education and Professional Education Courses were retrieved from the Professional Regulatory Commission through a request letter. Results were analyzed using Mean, t-test, and Pearson Moment Correlation Coefficient.
This study was conducted at Jose Rizal Memorial State University-Katipunan Campus, Katipunan, Zamboanga del Norte, Philippines.
Results and Discussion
This section presents the discussion of results and recommendations. This deals with the presentation of results and discussion of the data gathered based on the research problem and hypotheses posited for this study.
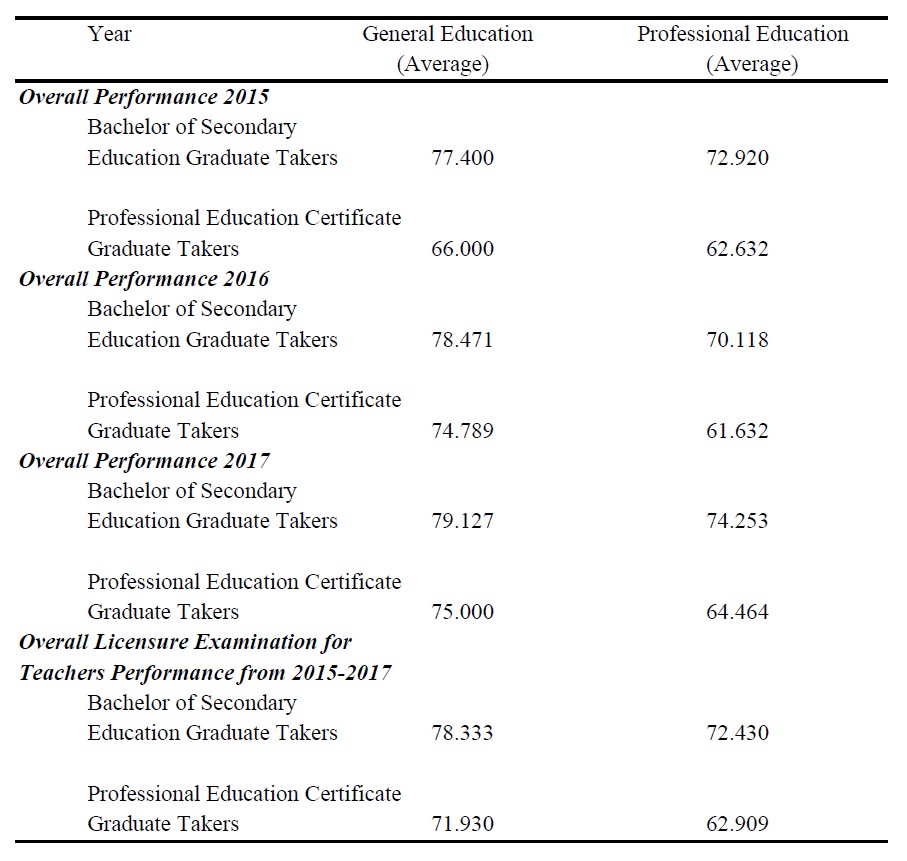
Table 1. Mean of General Education and Professional Education Courses Results in the Licensure Examination for Teachers by Bachelor of Secondary Education Graduate Takers and Professional Education Certificate (PEC) Program Graduate Takers per year.

In 2015, the result of the Bachelor of Secondary Education (BSEd) Graduate Takers in General Education Courses obtained a mean general average of 77.400 which is higher compared to the mean general average in Professional Education Courses which is 72.920 while the results of Professional Education Certificate Program (PEC) Graduate Takers obtained a mean general average of 66.000 in General Education Courses which is higher compared to Professional Education Courses which is 62.632.
In 2016, the BSEd Graduate Takers obtained a mean general average of 78.471 in General Education Courses which is also higher than the mean general average of 70.118 in Professional Education Courses while the PEC Graduate Takers obtained a mean of 74.789 in General Education Courses which is higher compared to the mean general average of 61.632 for the Professional Education Courses.
In 2017, the BSEd Graduate Takers obtained a mean of 79.127 for General Education Courses and a mean of 74.253 in Professional Education Courses while the PEC Graduate takers obtained a mean of 75.000 for General Education Courses and a mean of 64.464 for Professional Education Courses.
The overall performance of BSEd Graduates from 2015 to 2017 obtained an overall mean general average of 78.333 for General Education Courses which is higher compared to 72.430 for Professional Education Courses. While those PEC Graduate Takers obtained an overall mean rating of 71.930 for General Education Courses and 62.909 for Professional Education Courses. Therefore, the performance of both BSED and PEC Graduate Takers in General Education Courses is higher compared to Professional Education Courses.
This finding conformed to the study of Antiojo (2017) which states that the LET takers achieved the highest rating in General Education Courses followed by Professional Courses.
Table 2. Test of Significant Difference on the Results Incurred by the Bachelor of Secondary Education Graduate Takers and Professional Education Certificate (PEC) Program Graduate Takers in General Education Courses
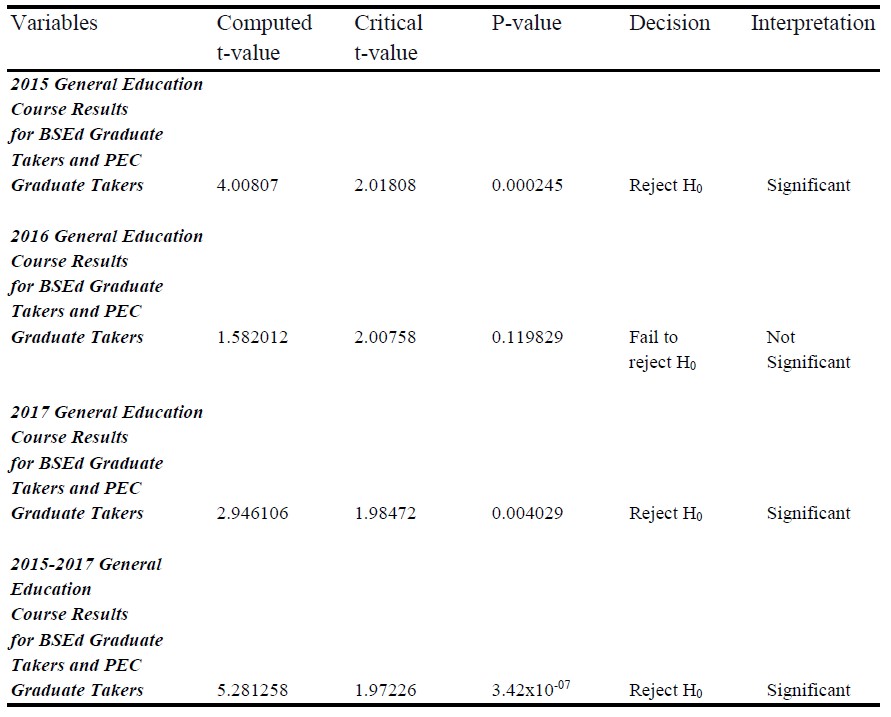
Presented in Table 2 is the test of significant difference on the results incurred by the Bachelor of Secondary Education (BSEd) Graduate Takers and Professional Education Certificate (PEC) Graduate Takers on General Education Courses in 2015.
The results on the table showed that the computed t-value is 4.00807 which is greater than the critical t-value of 2.018082 which rejects the null hypothesis. Therefore, there is a significant difference in the results of the Licensure Examination for Teachers (LET) in General Education Courses among BSEd and PEC Graduate takers. This implies that General Education Course results for this year differs.
In 2016, the computed t-value is 1.582012 is lesser than the critical t-value of 2.007584 which means that there is no significant difference in the results of the Licensure Examination for Teachers (LET) in General Education Courses among BSEd and PEC Graduate takers. This means that their General Education course result did not differ at all.
In 2017, the computed t-value of 2.946106 is greater than the critical t-value of 1.984723 which means that there is a significant difference in the results of the Licensure Examination for Teachers (LET) in General Education Courses among BSEd and PEC Graduate Takers. For this year, The General Education course result differs.
The overall results of the Test of Significant Difference on the Results Incurred by the BSEd and PEC Graduate Takers in General Education Courses from 2015 to 2017 have a computed t-value of 5.281258 which is greater compared to the critical t-value of 1.972268 which resulted in the rejection of the null hypothesis. Therefore, there is a significant difference in the results of the Licensure Examination for Teachers in General Education Courses among BSEd and PEC Graduate Takers. This means that the General education Course Results of the BSEd Graduate Takers is higher compared with that the result of the PEC Graduate Takers.
Table 3. Test of Significant Difference on the Results Incurred by the Bachelor of Secondary Education Graduate Takers and Professional Education Certificate (PEC) Program Graduate Takers on Professional Education Courses
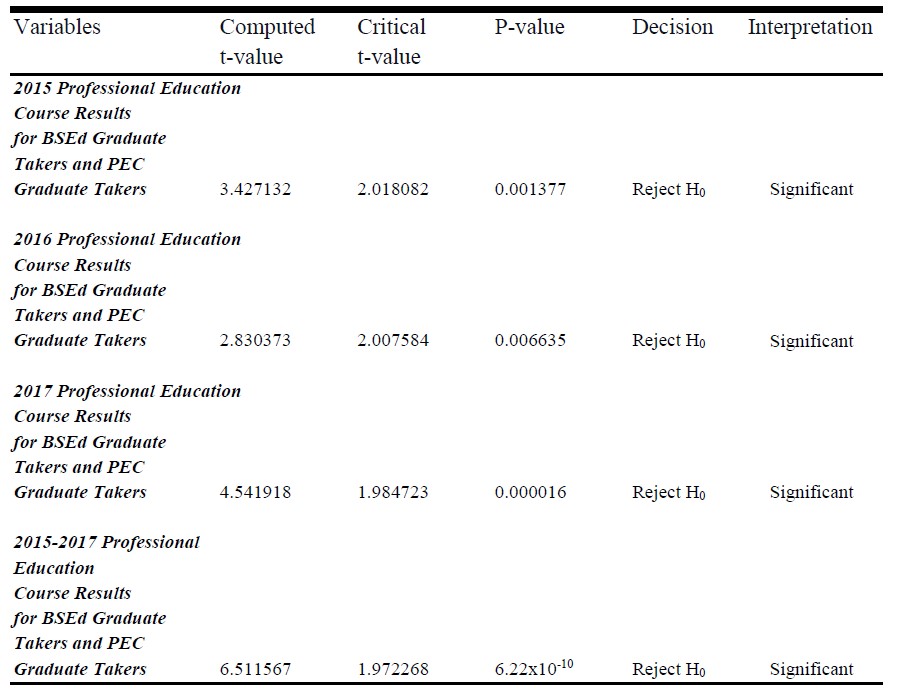
Presented in Table 3 is the test of difference on the Results incurred by the Bachelor of Secondary Education (BSEd) Graduate Takers and Professional Education Certificate (PEC) Graduate Takers on Professional Education Courses. The table showed that the result is constantly significant. This means that the Professional Education result between the two takers differ.
For the overall results from 2015-2017, the computed t-value of 6.511567 is greater than the critical computed t-value of 1.972268 which means that there is a significant difference in the results of the Licensure Examination for Teachers on Professional Education Courses among Bachelor of Secondary Education and Professional Education Certificate Program (PEC) Graduate Takers. It implies that their Professional Education Course Results differ.
Graph 1. Test of significant relationship between the general education and professional education LET results of 2015: Education Graduates and PEC Graduates.
Correlation between General Education and Professional Education Results
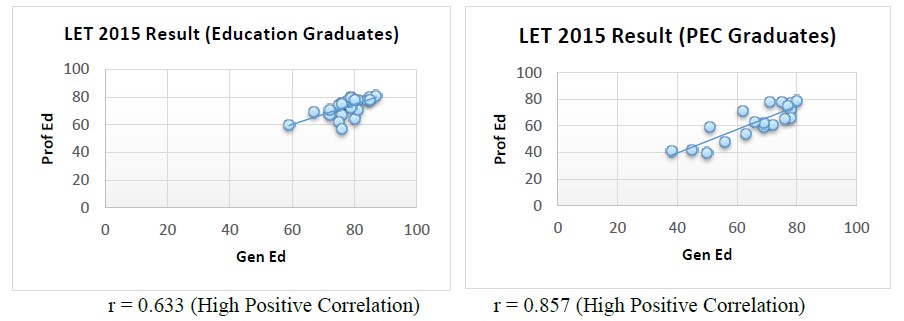
The graphs show that the general education courses and professional education courses result in the 2015 Licensure Examination for Teachers for both Education Graduates and PEC graduates have high positive correlation. This indicates that the general education course result and professional education course result are directly proportional. It means as general education course result is high, the professional education course result will follow.
Graph 2. Test of significant relationship between the general education and professional education LET results of 2016: Education Graduates and PEC Graduates. Correlation between General Education and Professional Education Results
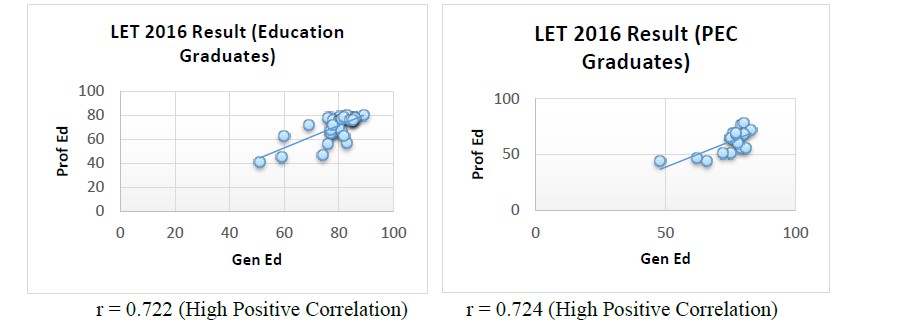
The graphs reveal that the general education courses and professional education courses result in the 2016 Licensure Examination for Teachers for both Education Graduates and PEC graduates have high positive correlation. This indicates that the general education course result and professional education course result are directly proportional. It means as general education course result is low, the professional education course result is also low.
Graph 3. Test of significant relationship between the general education and professional education LET results of 2017: Education Graduates and PEC Graduates. Correlation between General Education and Professional Education Results
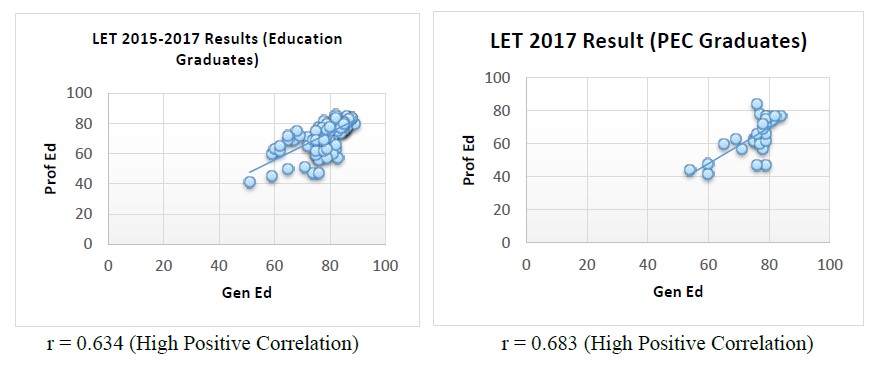
The graphs depict that the general education courses and professional education courses result in the 2017 Licensure Examination for Teachers for both Education Graduates and PEC graduates have high positive correlation. This indicates that the general education course result and professional education course result are directly proportional. It means as general education course result increases, the professional education course result also increases.
Graph 4. Test of significant relationship between the general education and professional education LET results from 2015-2017: Education Graduates and PEC Graduates. Correlation between General Education and Professional Education Results
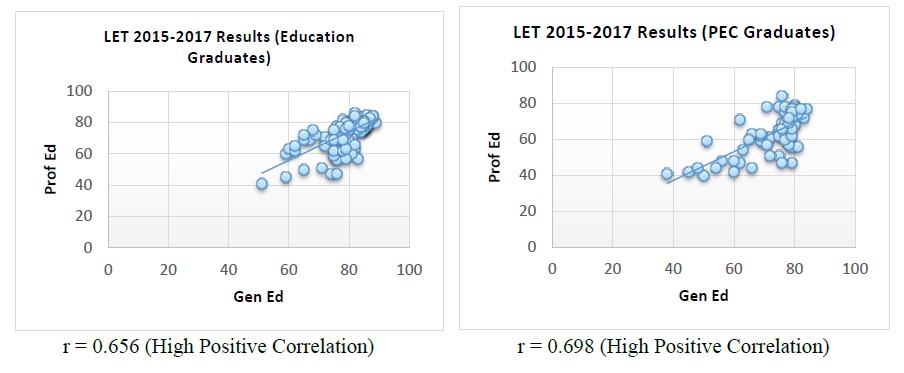
The graphs depict that the general education courses and professional education courses result from 2015 - 2017 Licensure Examination for Teachers for both Education Graduates and PEC graduates have high positive correlation. This indicates that the general education course result and professional education course result are directly proportional. It means as general education course result increases, the professional education course result also increases.
Conclusion
The general education courses and professional education courses result from 2015 - 2017 Licensure Examination for Teachers for both Education Graduates and PEC graduates have high positive correlation. Therefore, both Education and PEC graduates get similar results for General Education and Professional Education Courses. There is a linear correlation between the general education and professional education results of the BSEd graduates which mean that as general education result increases/decreases, the professional education result tends to increase/decrease as well. This means further that the general education and professional education results of PEC graduates are linearly related. It is concluded that while general education results improve or deteriorate, professional education outcomes likely to improve or deteriorate as well. There is a significant difference in the results of the Licensure Examination for Teachers on Professional Education Courses among BSEd and Professional Education Certificate (PEC) Graduate Takers. It is concluded that BSEd Graduate takers' Professional Education Course rating is higher than PEC Graduate takers' Professional Education Course rating.
Recommendation
Based on the findings and conclusions, this study recommends that the College of Education should enhance the Review Program, especially for the PEC Program completer focusing on the professional education courses.
References
Alova, C. A. (2021). Performance of College of Education graduates in the licensure examination for teachers: A descriptive study. Academia Letters. https://doi.org/10.20935/al4087
Amanonce, J. T., & Maramag, A. M. (2020). Licensure examination performance and academic achievement of teacher education graduates.International Journal of Evaluation and Research in Education (IJERE), 9(3), 510. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijere.v9i3.20614
CHED Memorandum Order No. 75 series of 2017 (Policies, Standards, and guidelines for Bachelor of Secondary Education (BSEd)
Chua, E. R., Andal, F. A., & Alexander, J. M. (2019). Readiness of Education Students in the Licensure Examination for Teachers (LET). Innovation in Language Learning. https://conference.pixel-online.net/library_scheda.php?id_abs=4050
Guinayen, V. K. (2014). Relationship of the Academic Performance to the Licensure
Examination for Teachers Performance of Mpspc Bsed Graduates. Mountain Province
State Polytechnic Colleges
Rabanal, G. C., (2016). Academic achievement and LET performance of the bachelor of elementary education graduates, University of Northern Philippines. International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, 6(6), 455-461.
Republic Act 7836: Philippine Teachers Professionalization Act of 1994. Retrieved from https://pcw.gov.ph/republic-act-7836-philippine-teachers-professionalization-act-of-1994/
Tan, C. (2016). IMPACT OF REVIEW ON THE PERFORMANCE OF GRADUATES IN THE LICENSURE EXAMINATION FOR TEACHERS, 2012-2014. e-Proceeding of the 4th Global Summit on Education GSE 2016 (e-ISBN 978-967-0792-07-1). 14-15 March 2016, Kuala Lumpur, MALAYSIA. Organized by http://worldconferences.net/home